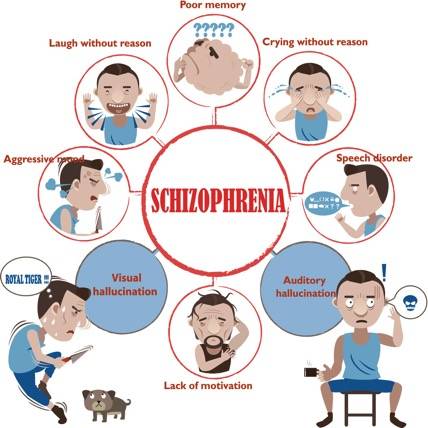
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by abnormal thoughts, perceptions, emotions, and behavior. It affects how individuals perceive and interpret reality, often resulting in a loss of contact with reality. Here is some information on the symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention of schizophrenia:
Symptoms:
- Delusions: False beliefs that are not based on reality. These delusions can be paranoid, grandiose, or related to control or reference.
- Hallucinations: Sensing things that are not real, most commonly auditory hallucinations (hearing voices), but they can also involve other senses.
- Disorganized thinking and speech: Difficulty organizing thoughts, speaking coherently, or connecting ideas logically.
- Grossly disorganized or abnormal motor behavior: Unpredictable or inappropriate behavior, including childlike silliness or agitation.
- Negative symptoms: Lack of motivation, social withdrawal, diminished emotional expression, and reduced speech.
Causes: The exact causes of schizophrenia are not fully understood, but it is believed to be a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Potential contributing factors include:
- Genetics: Having a family history of schizophrenia increases the risk.
- Brain chemistry and structure: Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, may play a role. Brain structure abnormalities have also been observed in individuals with schizophrenia.
- Environmental factors: Prenatal complications, exposure to viruses or toxins, and stressful life events may contribute.
Treatment: Schizophrenia is a chronic condition that typically requires lifelong management. The primary treatments include:
- Medications: Antipsychotic medications are the mainstay of treatment, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent relapses.
- Psychosocial interventions: Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), family therapy, and social skills training can help individuals cope with symptoms, manage stress, and improve functioning.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases or during acute episodes, hospitalization may be necessary for stabilization and ensuring safety.
Prevention: Prevention strategies for schizophrenia are challenging due to the complex nature of the disorder. However, some approaches may help reduce the risk or delay onset:
- Early intervention: Recognizing and addressing early signs and symptoms can improve outcomes and minimize the impact of the illness.
- Minimizing stress: Managing stress levels and building resilience may be beneficial, as stress can potentially trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
- Healthy lifestyle: Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding substance abuse can promote overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk.
It’s important to note that schizophrenia is a complex condition, and treatment plans should be tailored to the individual in collaboration with mental health professionals. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of schizophrenia, it is advisable to seek professional help for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.